Back to Special Relativity
Contents
- Principle of Time Dilation
- Example with Orange and Red Spacecraft
- Lifetime of a Muon
- Spacetime Diagram of Time Dilation
- Derivation of Time Dilation from the Lorentz Transformations
Principle of Time Dilation
- Δt′ = γ Δτ, where
- γ is the Lorentz Factor
- γ = 1 /√ (1 – v2/c2)
- Δτ (delta tau) is the elapsed time between events in an inertial reference frame S in which the events occur at the same location.
- τ is the proper time of an event, the time recorded by a clock in the event’s rest frame.
- Δt′ is the elapsed time between the events in an inertial reference frame in which frame S moves at constant velocity v.
- Δt′ is the coordinate time interval between the events.
- γ is the Lorentz Factor
- The Principle of Time Dilation follows directly from the Lorentz Transformation. See derivation below.
Example with Orange and Red Spacecraft
- In the Example involving Orange and Red Spacecraft, Orange transmits a light beam that reflects off a mirror and receives the reflection back two seconds later. In Red’s reference frame the same event takes 3 ⅓ seconds.

- Three Ways of Doing the Math:
- Calculation using Time Dilation Formula
- Δt′ = γ Δτ
- Δt′ = 1.66667 x 2 = 3 ⅓
- where γ = 1/√[1 – 0.82] = 1.66667.
- Calculation using Lorentz Transformations
- Δt′ = γ(Δt – vΔx/c2)
- 1.66667(2 – 0) = 3 ⅓
- Where Δx = 0.
- Calculation using the Invariance of the Spacetime Interval
- -(c Δt)2 + Δx2 + Δy2 + Δz2 = -(c Δ′t)2 + Δ′x2 + Δ′y2 + Δ′z2
- -(2 c)2 + 02 = -(Δt′ c)2 + (8 108)2
- Mathematica command:
- Solve[-(2 c )2 + 02 == -(tp c)2 + (8 108)2, tp, Assumptions → {c == 3 108} && tp > 0]
- tp = 10/3.
- Solve[-(2 c )2 + 02 == -(tp c)2 + (8 108)2, tp, Assumptions → {c == 3 108} && tp > 0]
- Calculation using Time Dilation Formula
Lifetime of a Muon
- A muon is an elementary subatomic particle like the electron but heavier. It lives only 2.2 microseconds before decaying into an electron and two neutrinos. Which is to say that it lives 2.2 microseconds in its own reference frame, where it’s at rest.
- A microsecond, abbreviated μs, is one millionth of a second.
- In an experiment at CERN in the 1970s muons were accelerated to 99.94 percent of the speed of light and their lifetimes measured (in the laboratory reference frame).
- Special Relativity predicts that the muon’s average lifetime in the laboratory frame is 63.518 microseconds because of time dilation.
- Δt′ = γ Δτ = 28.8718 x 2.2 = 63.518 μs
- where γ = 1 /√ (1 – 0.99942) = 28.8718.
- Δt′ = γ Δτ = 28.8718 x 2.2 = 63.518 μs
- Muons lived an average of 64 microseconds in the CERN experiment.
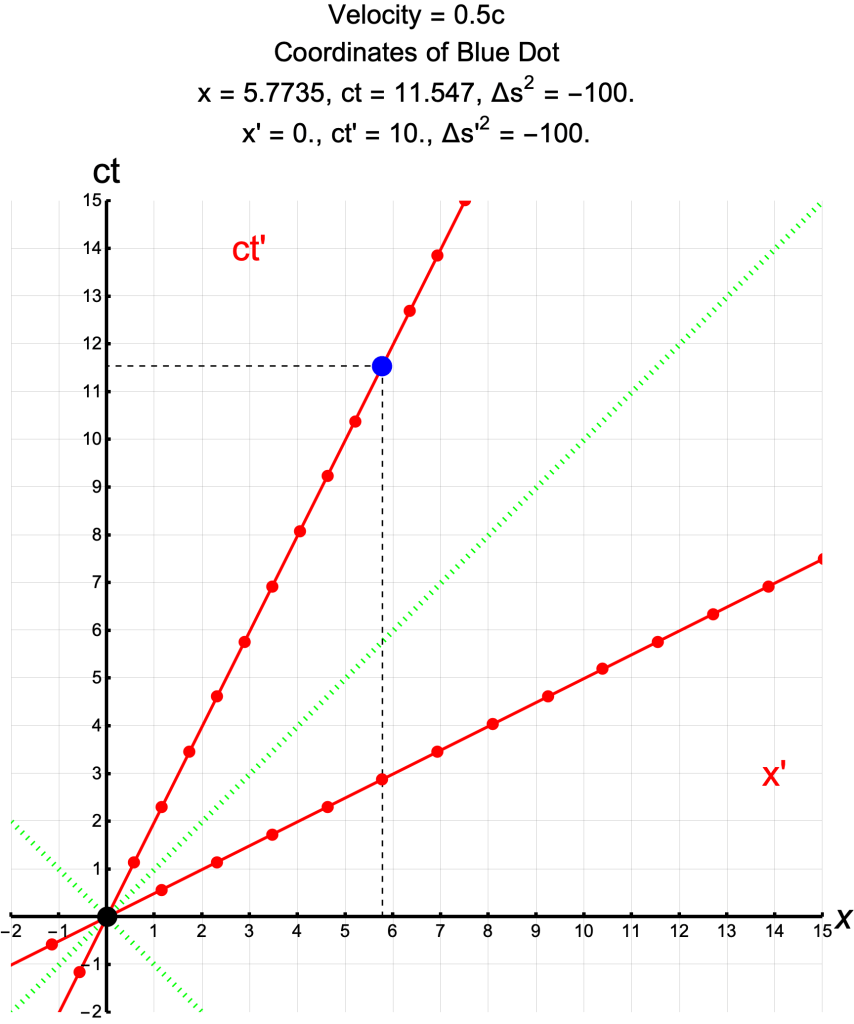
Spacetime Diagram of Time Dilation
- The interval between the black and blue events is 10 seconds in S′ (count the red dots) and 11.547 seconds in S.
- The events occur at the same location in S′ (at x′ = 0).
Derivation of Time Dilation from the Lorentz Transformations
- Δt′ = γ(Δt – vΔx/c2)
- Lorentz Transformation for interval of time
- Δx = 0
- Measurement of time interval is made at the same location in unprimed frame
- Δt′ = γ(Δt – 0)
- From 1 and 2
- Δt′ = γ Δt
- From 3
- Δt′ = γ Δτ
- Δτ = Δt